Case History:
Well-demarcated parotid mass.
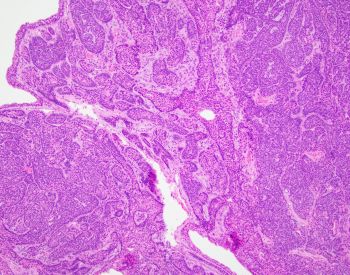
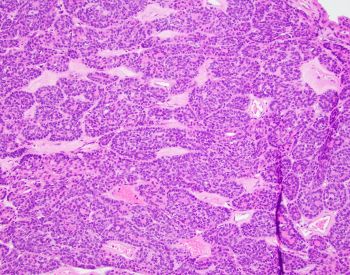
In the absence of invasion, what is the diagnosis?
A. Cellular pleomorphic adenoma
B. Tubulotrabecular basal cell adenoma
C. Intercalated duct hyperplasia/adenoma
D. Epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma
Correct Answer: B. Tubulotrabecular basal cell adenoma
Discussion:
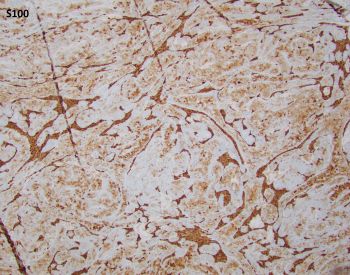
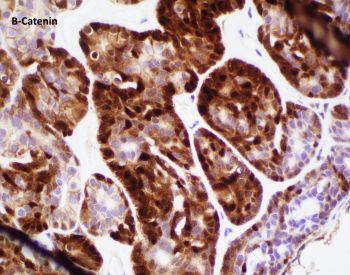
Basal cell adenoma is a benign salivary gland neoplasm comprised of luminal/epithelial and predominant abluminal/myoepithelial cell population (i.e. biphasic). CTNNB1 mutation is commonly seen with tubulotrabecular BCA (hence the nuclear expression), and a subset of them has spindled myoepithelial cell-derived stroma that is strongly and diffusely immunoreactive to S100 (Figure). This is usually absent in the membranous subtype which commonly has CYLD1 gene mutation, thus lacking nuclear beta catenin expression. Peripheral tissue, perineural or angioinvasion differentiates adenomas from carcinomas.
References:
Seethala R, Fonseca I, Jo VY et al. Chapter 4: Basal cell adenoma. In: WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Head and neck tumours. Lyon (France): International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2023. (WHO classification of tumours series, 5th ed.; vol. 9). https://publications.iarc.who.int/629.
Case contributed by: Melad N. Dababneh, M.B.B.S., Assistant Professor, Anatomic Pathology